Book Appointment Now


The Truth About Erectile Dysfunction and Its Affects on Sex Life
Erectile dysfunction is number 1 culprit making it difficult to keep a firm enough erection to have sex. This worsens both your sexual activity and quality of life. But no worries, medications and other treatments are available.

What is erectile dysfunction?
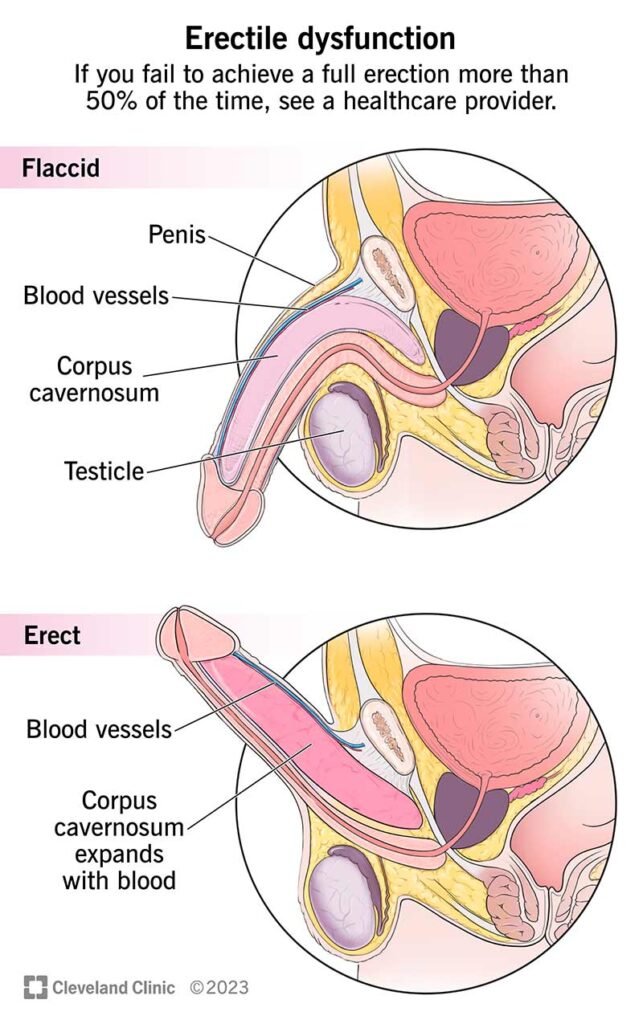
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a type of penile disorder. It affects the ability to get and maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.

Your feelings play a major role in getting and maintaining an erection. Feeling relaxed, confident and aroused is essential. But it’s normal to sometimes have erection issues. Erection problems can occur if you feel nervous, anxious, frustrated or tired. Drinking alcohol and/or using substances can also have an effect. It can also result from other conditions or as a side effect of certain medications or cancer treatments.
Erectile Dysfunction, where it come from?
In the past, erectile dysfunction was commonly believed to be caused by psychological problems. It is known today that, for most men, erectile dysfunction is caused by physical problems, usually due to the blood supply to the penis. Many advances have occurred in both diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction.
ED may affect up to 20 million people in the U.S. The condition’s prevalence is over 50% in those over 50 years old and increases with a person’s age.
Most cases of erectile dysfunction (ED) arise secondarily, indicating a change from normal erectile function to persistent issues, often due to physical factors. Primary ED, where a person has never achieved an erection, is rare and can stem from psychological or physical conditions.
Common causes of ED
Consulting a medical professional is crucial for those experiencing persistent erection problems, as underlying medical issues may be the cause. Common causes of ED include:
- heart disease
- diabetes
- high blood pressure
- obesity
- Parkinson’s disease
- multiple sclerosis
- hormonal disorders
- pelvic or spinal cord injuries
- pelvic radiation therapy
- Atherosclerosis, which narrows penile arteries and restricts blood flow necessary for erections, is also a typical vascular issue
- Prostate problems
- Hypogonadism in association with a number of endocrinologic conditions
- High levels of blood cholesterol
- Low levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein)
- Chronic sleep disorders (obstructive sleep apnea, insomnia)
- Drugs
- Neurogenic disorders
- Peyronie’s disease (distortion or curvature of the penis)
- Priapism (inflammation of the penis)
- Depression
- Alcohol use
- Lack of sexual knowledge
- Poor sexual techniques
- Inadequate interpersonal relationships
- Many chronic diseases, especially renal failure and dialysis
- Smoking, which exacerbates the effects of other risk factors, such as vascular disease or hypertension
Certain prescription medications, such as those for high blood pressure, heart conditions, anxiety, depression, opioids, cancer treatments, anticholinergics, and hormones, can also lead to ED.
Physical causes account for 90% of ED cases, while psychological factors are less common but still significant. Psychological factors contributing to ED can include fear of intimacy, depression, and general anxiety. Sexual performance anxiety is a prevalent psychological factor affecting males with ED.
It’s important to recognize the potential overlap between physical and psychosocial causes of ED. For example, obesity can impact blood flow (physical cause) and self-esteem (psychosocial cause), both affecting erectile function.
What is the best way to fix erectile dysfunction?
The initial step involves identifying its root with the guidance of a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Options may include:
- Engaging in Cardiovascular Exercise: Regular vigorous activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or jump rope sessions, at least 45 minutes, three times weekly, may reverse mild cases of ED.
- Practice Kegel or Pelvic Floor Exercises and Pilates.
- Quitting Smoking: For those with mild ED, stopping smoking can lead to improvement over several months.
- Consulting with a sex therapist.
- Oral medications such as sildenafil (Viagra®), vardenafil (Levitra®), tadalafil (Cialis®), or avanafil (Stendra®), which enhance blood flow to the penis and typically start working within an hour.
- Penile low-intensity focused shockwave therapy (LiSWT): This noninvasive treatment uses sound waves to improve blood flow, with noticeable results possibly taking up to two months.
- Injecting medications directly into the penis to induce an erection, such as alprostadil (Caverject®), papaverine (Papacon®), phentolamine (Regitine®), or combinations thereof, which start working within 10 minutes.
- Using a vacuum constriction device (penis pump) that achieves results almost immediately.
- Testosterone replacement therapy, available as gel, injection, patches, or pellets, with effects noticeable within four weeks.
- Undergoing a penile implant procedure, where a device is surgically inserted to enable erections without affecting sensation, urination, or orgasm.
- Trying Mediterranean diet which can benefit sexual health
Can masturbation cause ED?
Masturbation cannot cause ED.
Recent research found that higher masturbation frequency and pornography use was weakly linked to ED.
How do couples cope with ED?


Erectile dysfunction can cause strain on a couple. Many times, men will avoid sexual situations due to the emotional pain associated with ED, causing their partner to feel rejected or inadequate. It is important to communicate openly with your partner. Some couples consider seeking treatment for ED together, while other men prefer to seek treatment without their partner’s knowledge. A lack of communication is the primary barrier for seeking treatment and can prolong the suffering. The loss of erectile capacity can have a profound effect on a man. The good news is that ED can usually be treated safely and effectively.
Embarrassment about sexual health issues often prevents men from seeking necessary medical attention, delaying the diagnosis and treatment of potentially serious underlying conditions. ED itself can signal underlying problems like heart disease, diabetes, or liver disease.
Since ED can be a forewarning symptom of progressive coronary disease, doctors should be more direct when questioning patients about their health. By asking patients more directly about their sexual function through conversation or a questionnaire during a checkup, doctors may be able to detect more serious health conditions sooner.